Algebraic paradox - Geometric graceli.
1. The difference between the sum of the cube and the square of the legs in relation to the cube or square of the hypotenuse progressively increases as the size of the sides of the legs and also increases or square to cube on cube.
2- In a sequential divisive process graceli this difference will always bring sequential infinitesimal numbers.
3. The sum of the cube of the legs always have a hypotenuse of irrational number, transcendental, infinitesimal.
4. When the sum of the squares of the legs is a prime number the hypotenuse is a transcendent irrational number. Ie the sum of the squares of the legs will never be equal to the square of the hypotenuse.
5- Most often the hypotenuse to the hub in relation to the sum of the cube of the legs will be a prime number.
6- In an equilateral triangle the sum of the squares of the legs will never be equal to the square of the hypotenuse.
7 In other words, what we have is an algebraic rather than geometric theory.
Geometry and dynamic oscillatory variations.
With two waves that propagate next to one another.
A crossing each other.
1- It can be two oscillatory waves with concave and convex movements and differentials. And indeterminate and alternate oscillatory flows.
2- Or even type spiral type movements that form the genetic code.
3- Or even the dog graceli Paradox [where it forms curved differential movements in all directions].
R [+, -, *, /] pr / pPr [n] * [i].
R [+, -, *, /] pr / pPr [n] * [i], MCC, mcx, mccdd, mcxdd, + [Fo].
Ray, progression, nth, imaginary numbers, concave and convex movement, dynamic and differential, and oscillatory flows.
1].
3 3 3
A + b = d h.
The sum hub of the legs is different from the hub of the hypotenuse, because in this case the hypotenuse will always be an irrational number, transcendental and infinitesimal.
3 3 3
Pa + PB = d Ph.
Why the progression of the sum of the cube of the legs is one, and the progression of the hub of the hypotenuse is another. Ie, increases as the size of the legs.
7 most beautiful functions graceli.
The sum of the collared peccary squared or cubed an equilateral triangle with a cathetus b cubed or squared, always have the square or cube of different hypotenuse.
These formulas bring new insight into the flat geometry, and incompatible between algebra and geometry.
2] Calculation transcendent sequences between functions.
Graceli calculations and their relationship [universal, sequential and transcendent].
The calculations graceli [sequence, transcendental, universal], and can also be a sequence limit calculation, or even be statistical averaging sums of x to y sequences.
Ie can be full, partial, limit, parts [initial, middle or final], it is a theory of limits of sequences, and a theory derived by progressions, logarithms, and even roots. And it is also a calculation of statistics and matrix.
And it can be composed, where a dividend dividend might be several dividers simultaneously.
Example. X / log y / y [n] + [x / 1 + p / px + py [n]] + [x / 1 + p + logx / p [n]] [n].
Or the same product or result divided by jumping sequences in relation to each other sequences, or sequences sums in this case have the transcendental calculation.
3]
Function general graceli of quantum and relativity.
As the radiation energy increases, and or plasma waves occurs on particles and an expansion energy, wave, particle, mass involved in the system increasing instability leading to a position uncertainty or time, or intensity increased with increasing energy in the system and produces an expansion in the mass, energy, field, load, inertia, particle system that has a curvy waves and oscillatory engagement with undetermined vibrations, this scale can occur both in the energy in photons, and space, and is proportional to the increase energy involved in the system, which have an action of vortices [a centrifugal action], and where this vortex force action tends to have a spiral shape expanding [see the same in relation to the cosmos], and this being divided by the speed from light.
Ie, we have a continuum and a unified system between quantum and restricted and general relativity.
That is, we
The expansion waves and particles and energy + function of uncertainty divided by a curved system of matter and fields represented by the function of general relativity. And that does not necessarily need to be in space, but in the fields, and the particle itself.
E + P + fi / RR / RG + ex / c
Energy particles + + + waves uncertainty function relativity / general relativity + index expansion / c
This function behind the unification between the quantum and relativity.
4]
The number of graceli to find the value of pi.
Graceli number theory.
Number of graceli. = G = 2.855993321445266 ................... * 1.1 = 3.141592653589793 ...................
It is an irrational number, transcendental, repeated sequences, and an infinitesimal number.
Pi divided by 1.1.
g = 2.855993321445266 ................... * 1.1 = pi = 3.141592653589793 .................. .
By nature is a sequential number and also an infinitesimal.
Note. For this number can be confirmed in sequential homes through nth pi, through spin, using the geometry calculation, algebra, trigonometry, derivatives, and various other branches.
Where the result is always a sequence of numbers.
5] sequence with endless repetition.
Dividend divided by divisor, then follows producer / splitter [n] = nth times following repeated and endless graceli.
1/1 + 0. 309309309309 [n] = 1.309309309309309, 1.618618618618, 1.927927927, 1.1237237237, 1.546454645464, 1.855885588558 ...................... ..
[Ad infinitum].
Paradoxo algébrico - geométrico de Graceli.
1- A diferença entre soma do cubo e do quadrado dos catetos em relação ao cubo ou quadrado da hipotenusa aumenta progressivamente conforme aumenta o tamanho dos lados dos catetos, e ou também aumenta de quadrado para cubo, de cubo em diante.
2- Num processo divisório seqüencial de graceli esta diferença sempre trará números infinitesimais sequenciais.
3- A soma do cubo dos catetos sempre terá uma hipotenusa de número irracional, transcendente, infinitésimo.
4- Quando a soma do quadrado dos catetos for um numero primo a hipotenusa será um numero irracional transcendente. Ou seja, a soma do quadrado dos catetos nunca será igual ao quadrado da hipotenusa.
5- Na maioria das vezes a hipotenusa ao cubo em relação a soma do cubo dos catetos será um numero primo.
6- Num triângulo eqüilátero a soma do quadrado dos catetos nunca será igual ao quadrado da hipotenusa.
7- Ou seja, o que temos é uma teoria algébrica e não geométrica.
Geometria e variações oscilatórias dinâmicas.
Com duas ondas que se propagam uma próxima da outra.
Uma cruzando a outra.
1- Pode ser duas ondas oscilatórias com movimentos côncavos e convexos e diferenciais. E fluxos oscilatórios indeterminados e alternados.
2- Ou mesmo de movimentos tipo espiral tipo que forma o código genético.
3- Ou mesmo do paradoxo Graceli do cachorro [onde se forma movimentos curvos diferenciais para todos os lados].
R [+, - , *, /] pr/pPr [n] *[i].
R [+, - , *, /] pr/pPr [n] *[i], mcc, mcx, mccdd, mcxdd, +[Fo].
Raio, progressão, enésimo, numero imaginário, movimento côncavo e convexo, dinâmica e diferencial, e fluxos oscilatórios.
As 7 funções mais belas de Graceli.
1].
3 3 3
A + b = d h.
A soma de cubo dos catetos é diferente do cubo da hipotenusa, por que neste caso a hipotenusa sempre será um número irracional, transcendente e infinitesimal.
3 3 3
Pa + PB = d Ph.
Por que a progressão da soma do cubo dos catetos é uma, e a progressão do cubo da hipotenusa é outra. Ou seja, aumenta conforme aumenta o tamanho dos catetos.
2,ou 3 2,ou 3 2,ou 3
cae + cbe = diferente da h
A soma do cateto a ao quadrado ou ao cubo de um triangulo eqüilátero com um cateto b ao cubo ou ao quadrado, sempre terá o quadrado ou o cubo da hipotenusa diferente.
Estas fórmulas trazem nova visão sobre a geometria plana, e incompatível entre a álgebra e a geometria.
2] Cálculo transcendente entre sequências de funções.
Cálculos de Graceli e sua relação [universal, sequencial e transcendente].
Os cálculos de Graceli [sequencial, transcendente, e universal], e que também pode ser um cálculo de limite de sequência, ou mesmo ser estatístico com média de somatórias de sequências de x até y.
Ou seja, pode ser integral, parcial, de limite, de partes [inicial, mediana ou final], é uma teoria de limites de sequências, e uma teoria de derivada por progressões, logaritmos, e mesmo de raízes. E é um cálculo de também de estatística e de matriz.
E pode ser composto, onde um dividendo pode vir a ser dividendo de vários divisores ao mesmo tempo.
Exemplo. X / log y / y [n], + [ x / 1 + p/px+py[n]] + [x / 1 + p+ logx / p [n]] [n].
Ou mesmo o produto ou resultado dividido por sequências que saltam umas em relação às outras sequências, ou somas de sequências, neste caso temos o cálculo transcendente.
3]
Função Graceli geral da quântica e relatividade.
Conforme aumenta a energia de radiação e ou plasmas sobre partículas e ondas ocorre uma dilatação na energia, ondas, partícula, massa envolvida no sistema aumentando uma instabilidade levando a uma incerteza de posição ou tempo, ou intensidade conforme aumenta a energia acrescida no sistema e que produz uma dilatação nas massa, energia, campo, cargas, inércia, partícula, ondas do sistema que tem um envolvimento curvilíneo e oscilatório com vibrações indeterminadas, esta envergadura pode ocorrer tanto na energia, nos fótons, e no espaço, e é proporcional ao acréscimo de energia envolvida no sistema, onde temos uma ação de vórtices [com ação centrífuga], e onde esta ação de força de vórtice tende a ter uma forma espiral em expansão [o mesmo vemos em relação ao cosmo], e sendo isto dividido pela velocidade da luz.
Ou seja, temos um continuum e um sistema unificado entre a quântica e as relatividades restrita e geral.
Ou seja, temos
A dilatação de ondas e partículas e energia + função da incerteza dividida por um sistema curvo por matéria e campos representado pela função da relatividade geral. E que não precisa ser necessariamente no espaço, mas dentro dos campos, e da própria partícula.
E + op + fi / RR / RG +ex /c
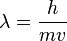 ,+
,+
 /
/  + ex / c
+ ex / c
Energia + ondas partículas + função de incerteza + relatividade restrita / relatividade geral + índice de expansão / c
Esta função trás a unificação entre a quântica e as relatividades.
4]
O numero de graceli para encontrar o valor de pi.
Teoria Graceli dos números.
Número de Graceli. = g = 2,855993321445266................... * 1.1 = 3,141592653589793...................
É um número irracional, transcendente, de sequências repetidas, e um número infinitesimal.
Divide-se pi por 1.1.
g = 2,855993321445266................... * 1.1 = pi = 3,141592653589793...................
Por natureza é um número sequencial e também é um infinitesimal.
Observação. Por este número é possível ser confirmado em enésimas casas sequenciais através de pi, através de derivadas, com uso na geometria, cálculo, álgebra, trigonometria, derivadas, e vários outros ramos.
Onde o resultado é sempre uma sequência de números.
5] Sequência com repetição infinita.
Dividendo dividido por divisor, depois segue produtor / divisor [n] enésima vezes = sequência Graceli repetidas e infinitas.
1/ 1+0. 309309309309 [n] = 1,309309309309309, 1,618618618618, 1,927927927, 1,1237237237, 1,546454645464, 1,855885588558........................
[ad infinitum].
6]Teorema de Graceli.
Teoremas de graceli.
Com o conjunto de inteiros positivos x, y, z,k e n com n maior que 2 para que satisfaça a equação.
teorema 1 de Graceli.
pP k pPk pPk
X + y = z
Teorema 2.
pP k pPk [i] pPk
X + y = z + 1
Teorema 3.
pP k pPk [i] p P k pPk
X + y + k = z + 1
pPk = progressão com expoente de progressão e k é um número comum para todos. Neste caso o expoente representa n.
7] função de abrangência de possibilidades de resultados.
P / logy/y [n] * [i ].[+u]
X = 0, 1, y, infinito, sG.
sG = sequência Graceli.